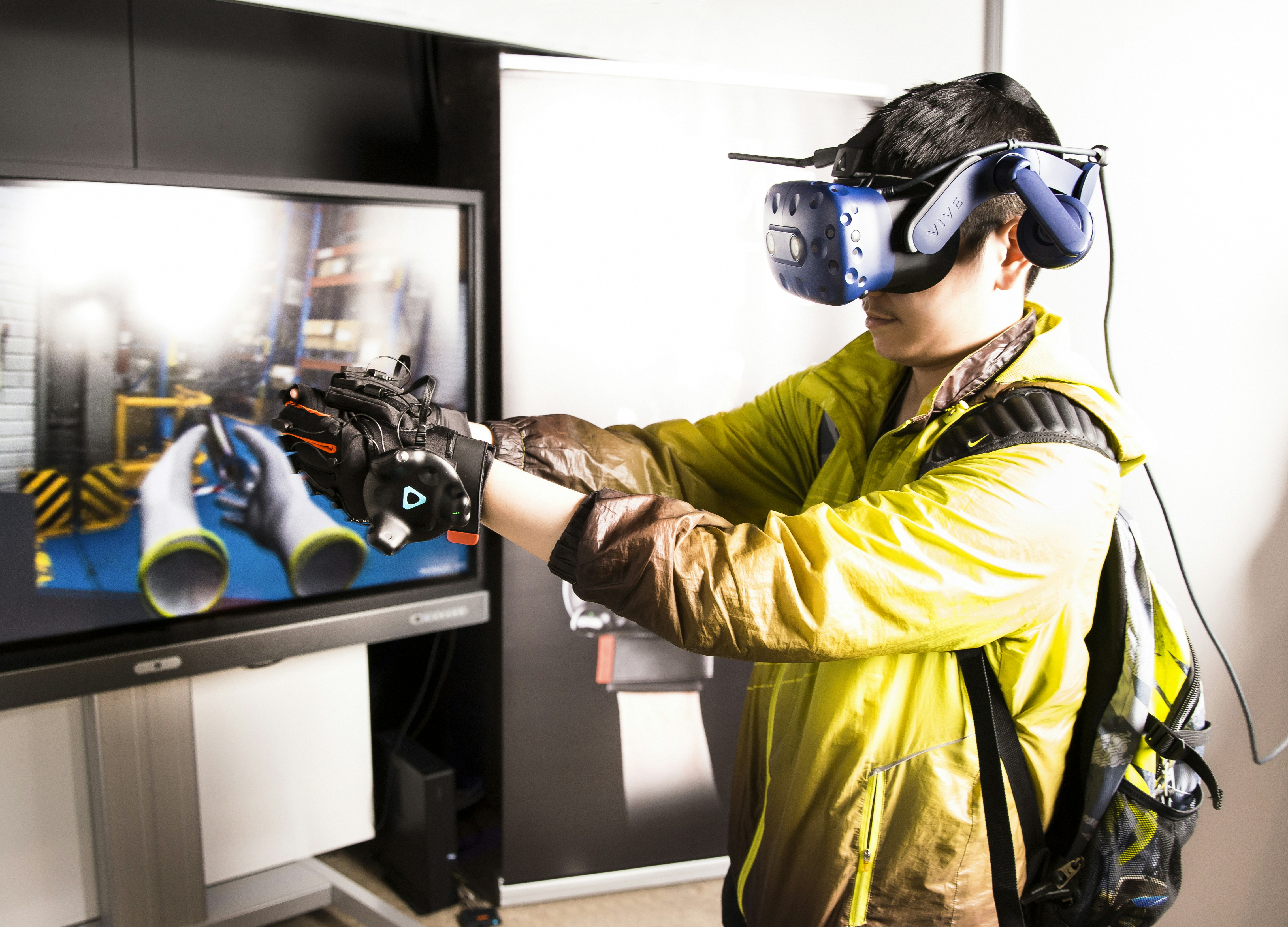
Introduction to Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) represents a transformative technological advancement that facilitates immersive experiences by simulating a three-dimensional environment. Leveraging advanced computing systems and sensory technology, VR allows users to engage with digital environments as if they were interacting with the real world. The integration of visual, auditory, and sometimes tactile feedback creates a compelling sense of presence, enabling users to explore expansive virtual realms.
The history of virtual reality can be traced back to the 1960s, when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland developed the first head-mounted display system, aptly named the “Sword of Damocles.” Although rudimentary by today’s standards, this pivotal invention sparked the imagination of researchers and technologists alike. During the 1980s and 1990s, VR garnered considerable attention in the gaming and entertainment sectors, with significant developments leading to the creation of the first VR arcade games and simulations. However, these early endeavors faced limitations due to the constraints of technology at the time, resulting in limited commercial success.
Fast forward to the 21st century, and advancements in computing power, graphics, and motion tracking have propelled virtual reality into mainstream awareness and utilization. Headsets from companies like Oculus, HTC, and Sony have made VR more accessible, while the expansion of mobile and standalone VR devices has further democratized this innovative medium. With state-of-the-art motion capture and high-definition visuals, contemporary VR not only enhances gaming experiences but also paves the way for applications in fields such as education, healthcare, and training.
As the technology continues to evolve, the potential applications for virtual reality are vast and varied. This introduction lays the foundation for a comprehensive examination of VR’s capacity to reshape sectors beyond just entertainment, influencing how we learn, work, and interact with one another.
The Role of Virtual Reality in Education
Virtual reality (VR) is swiftly emerging as a transformative tool in the educational landscape, offering innovative ways to engage learners and enhance their learning experiences. By integrating VR into the curriculum, educators can create immersive environments that allow students to explore concepts and ideas beyond traditional classroom boundaries. One significant application of VR in education is the ability to take virtual field trips, enabling students to visit historical sites, natural wonders, or even outer space, all from the comfort of their classrooms. This not only makes learning more exciting but also fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Moreover, VR can facilitate interactive learning environments where students actively engage with the material. These virtual classrooms can simulate real-world scenarios that might otherwise be challenging to replicate in a brick-and-mortar setting. For instance, medical students can practice surgical techniques in a risk-free VR simulation, while chemistry students can conduct experiments in a virtual laboratory, gaining hands-on experience without the associated dangers of real-life experimentation.
Another noteworthy advantage of incorporating VR into education is its capacity for simulation-based training. This approach is particularly beneficial for vocational education, where students can gain practical skills in a controlled setting. Industries such as aviation and emergency services utilize VR for training exercises, allowing individuals to learn critical skills and make decisions in high-pressure situations without the potential for real-world consequences.
Furthermore, research indicates that using VR in education can lead to enhanced engagement and improved retention rates among students. The immersive nature of virtual experiences tends to capture learners’ attention better than traditional methods, making it easier for them to absorb information. By leveraging VR technology, educators can create a dynamic and effective learning atmosphere that prepares students for the complexities of the modern world.
Virtual Reality in Entertainment
Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a revolutionary force within the entertainment industry, dramatically reshaping the way audiences engage with content. One of the most pronounced applications of VR lies in gaming, where immersive experiences provide players with unparalleled interactivity. Unlike traditional video games, which offer limited perspectives, VR games allow participants to step directly into the virtual environment, fostering an intimate connection with the storyline and characters. This shift in interaction not only enhances gameplay but also deepens the emotional involvement of the player.
Moreover, the evolution of immersive movies has laid the groundwork for a new breed of storytelling. Filmmakers are now exploring VR to create narratives in which viewers become active participants rather than passive observers. By utilizing 360-degree cameras and immersive soundscapes, these films transport audiences into the heart of the action, allowing them to experience events from various angles and perspectives. This engagement not only heightens the sense of presence but also revolutionizes how stories are told, enabling narratives that adapt to the audience’s intuitive reactions.
In addition to gaming and film, virtual concerts represent another exciting frontier in the entertainment sector. Artists are leveraging VR to create live performances that can be accessed from anywhere in the world. Attendees can enjoy the concert experience without the need for physical presence, offering a unique blend of accessibility and engagement. Not only does this format cater to a broader audience, but it also enables innovative interactions, such as virtual meet-and-greets and fan-driven experiences.
The ongoing advancements in VR technology promise to enhance audience engagement further, paving the way for a more interactive and personalized entertainment landscape. As creators continue to explore the vast potential of VR, we can anticipate a future where storytelling transcends traditional boundaries, harnessing the power of immersive experiences to captivate and connect with audiences on a profound level.
Applications of Virtual Reality in Professional Training
Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative technology in professional training across numerous sectors, including healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing. One of the key advantages of VR in this context is its ability to provide immersive, simulation-based training experiences that enhance learning outcomes while minimizing risks typically associated with conventional training methods. This innovative approach allows professionals to practice skills in a controlled, virtual environment where they can make mistakes without the repercussions that would occur in real-life scenarios.
In the healthcare industry, for instance, VR is revolutionizing the way medical professionals are trained. Surgeons can utilize VR simulations to practice intricate procedures, allowing them to hone their skills before working on actual patients. This not only boosts confidence but also significantly reduces the likelihood of errors during real operations. Companies such as Osso VR have developed comprehensive platforms that transport medical personnel into lifelike surgical environments, enabling them to refine their techniques in a risk-free setting.
Similarly, in the aviation sector, airlines and training institutions are leveraging VR for pilot training. The use of VR flight simulators enables pilots to experience diverse flying conditions and emergency situations they may not encounter often. This enhances their preparedness and decision-making abilities in critical moments. Institutions such as Boeing have adopted VR technology to supplement traditional flight training programs, resulting in improved safety and reduced training costs.
Moreover, the manufacturing industry is witnessing gains from VR as well. Companies like Ford and Volkswagen are employing VR solutions to train assembly line workers, who can familiarize themselves with complex machinery and assembly processes. This application not only enhances skill development but also decreases the time and financial resources needed for traditional training methods, such as hands-on workshops or instructor-led sessions.
As industries continue to explore the capabilities of VR, the trend of integrating this technology into professional training is expected to grow, promoting safer, more effective, and cost-efficient training methodologies.
Virtual Reality in Therapy and Mental Health
Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative tool in the realm of therapy and mental health, offering innovative approaches to treat a variety of psychological conditions. This immersive technology allows patients to engage in controlled environments that replicate real-world scenarios, providing a unique platform for therapeutic interventions. One of the most prominent applications of VR in therapy is exposure therapy, which is particularly effective for individuals experiencing phobias, anxiety, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). By gradually exposing patients to their fears in a safe, virtual setting, therapists can help desensitize them and foster coping strategies.
Research studies have highlighted the effectiveness of VR in pain management as well. For instance, virtual reality environments can divert attention from pain stimuli, reducing perceived pain levels during medical procedures. This is beneficial not only for patients suffering from chronic pain but also those undergoing acute treatments that can be distressing. By immersing patients in engaging environments, VR helps lessen anxiety and enhances their overall experience.
Several case studies underscore the efficacy of VR in treating mental health issues. For example, a research project conducted by Harvard Medical School demonstrated that patients using VR for exposure therapy reported significant reductions in anxiety symptoms over traditional therapy methods. Another study from the University of Washington revealed that VR can significantly decrease symptoms associated with social anxiety by allowing users to practice social interactions in a risk-free environment. However, while the benefits of VR in therapy are promising, it is crucial to approach its implementation thoughtfully, ensuring that it complements traditional therapies rather than replaces them. The integration of virtual reality into mental health treatment showcases an exciting opportunity to innovate therapeutic methodologies, potentially leading to enhanced patient outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Virtual Reality
Despite the transformative potential of virtual reality (VR) across various sectors, including education and entertainment, several challenges and limitations hinder its widespread adoption. One significant barrier is accessibility. Although VR technology has advanced rapidly, high-quality VR systems often require substantial financial investment, making them inaccessible to many users, particularly in lower-income demographics. The costs associated with not just the hardware, such as headsets and sensors, but also the software necessary for optimal experiences can be prohibitive for educational institutions and casual users alike. This economic disparity can lead to unequal access to the benefits VR can provide.
Furthermore, the need for exclusive physical space to fully utilize VR setups poses another challenge. Many users lack the necessary environment to engage with VR safely, which further limits its adoption. Additionally, as the VR industry evolves, the technology is constantly changing, necessitating continuous updates and upgrades that can add to the financial burden faced by consumers and organizations. As a result, many potential users may be hesitant to invest in VR, fearing they may need to replace equipment or software frequently.
Another concern associated with prolonged use of VR is the potential health risks it poses. Users often experience discomfort such as motion sickness, eye strain, and fatigue during extended sessions. Research shows that different individuals may react to VR exposure variably, which could dissuade some users from engaging with this technology regularly. Addressing these health concerns is crucial for enhancing user experiences and ensuring long-term viability. It is vital that continued research and development in the field of virtual reality aim to mitigate these challenges, ensuring that advancements in this transformative technology can truly benefit a wider audience.
Future Trends in Virtual Reality
The landscape of virtual reality (VR) is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and increasing adoption across various sectors. One salient trend is the integration of augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) into the broader VR ecosystem. While VR immerses users in a fully digital environment, AR overlays digital information onto the real world, and MR merges both seamlessly. This convergence aims to enhance user experience, allowing individuals to interact with digital content in their physical surroundings. As the lines between these realities blur, we can anticipate applications that harness the strengths of each, promoting an enriched interaction interface.
Another defining trend involves the expansion of VR in educational settings. Educational institutions are beginning to embrace VR for immersive learning experiences that foster engagement. For instance, virtual field trips and simulations position students in realistic scenarios that can enhance understanding and retention of complex subjects. Furthermore, as VR technology becomes more accessible, institutions may adopt it for remote learning, enabling global collaboration without geographical constraints. This shift signifies the potential of VR not only as a tool for entertainment but also as a powerful educational asset.
In the realm of entertainment, gaming continues to lead the charge for VR adoption, with developers striving to create more immersive and interactive experiences. Beyond gaming, we anticipate growth in VR experiences for movies and live events, where audiences can feel a part of the action. Additionally, the burgeoning trend of social VR is poised to revolutionize how people connect, allowing users to experience events collectively despite distance barriers.
Industries such as healthcare, real estate, and training simulations are also expected to explore innovative VR solutions. Healthcare professionals can practice surgical procedures in low-risk virtual environments, while real estate agents can provide virtual home tours to prospective buyers. As these technologies advance, it becomes evident that VR will continue to transform how we learn, play, and connect, heralding a new era in digital interaction.
Conclusion: The Impact of VR on Our Lives
As we delve into the potential of virtual reality, it is evident that this innovative technology is reshaping various aspects of our lives. From education to entertainment and beyond, VR serves as a catalyst for substantial change. In the educational realm, virtual reality provides immersive learning experiences that engage students in ways traditional teaching methods cannot. Through virtual simulations, learners can explore historical events, navigate complex scientific concepts, or practice real-life skills in a safe environment. This interactive approach enhances retention and fosters a deeper understanding of the subjects being studied.
In the entertainment industry, virtual reality has transformed how we engage with content. Gamers can be transported into different worlds, experiencing heightened realism and interactivity that enhances their overall experience. Movies and virtual concerts are also evolving thanks to VR, allowing audiences to immerse themselves in narratives and performances like never before. By fostering these transformative experiences, virtual reality has the potential to redefine entertainment as we know it.
Moreover, the applications of VR extend into various fields such as healthcare, architecture, and even mental health therapy, where immersive experiences can lead to better patient outcomes or innovative design models. As we look to the future, the imperative to embrace virtual reality and its capabilities becomes increasingly apparent. This technology is poised to unlock new avenues for personal and professional development across multiple domains.
In conclusion, as virtual reality continues to evolve and integrate into our everyday lives, it is essential for individuals and organizations to stay informed about its offerings. The transformative nature of VR presents opportunities that can significantly enhance our experiences, and being proactive in understanding its advantages is crucial for future growth and adaptation in an increasingly digital world.
Call to Action: Embrace the Virtual Revolution
The advent of virtual reality (VR) technology signifies a monumental shift in how we engage with the world around us. As we explore the potential of VR, it is imperative for individuals, educators, and organizations alike to embrace this innovative medium. From enhancing the educational landscape to redefining entertainment and improving healthcare, the applications of VR are vast and varied. The time is ripe for everyone to actively participate in this virtual revolution and harness the benefits this technology has to offer.
To fully grasp the capabilities of VR, readers are encouraged to seek out experiences that allow them to immerse themselves in this transformative environment. Numerous platforms are available, offering a range of VR content from educational simulations to dramatic gaming experiences. Resources such as SteamVR, Oculus, and various educational VR applications can provide introductory experiences for those curious about the technology. Engaging with VR firsthand can effectively illustrate its potential. Through various VR experiences, users can experience biology lessons in 3D, embark on historical journeys, or enjoy games that challenge the boundaries of traditional play.
Moreover, supporting VR initiatives within educational institutions, gaming communities, and healthcare systems is critical. Partnerships between technology developers and educators can foster the creation of curricula that embed VR learning tools. By advocating for such integration, individuals contribute to shaping a future where VR not only entertains but also educates and heals. The involvement in community discussions, attending VR expos, or participating in online forums dedicated to VR innovation can significantly bolster the growth of this technology. The collective effort can pave the way toward a more immersive and interactive experience in various fields, ultimately enhancing human connection and understanding.